alcohol is bad for sleep
- Key Takeaways:
- Alcohol can be a sleep aid but its not good for health. Feeling sleepy and getting a “good night of rest” are different. Even a smidgen before bed can throw off your Zzz’s.
- Imagine alcohol as that friend who overstays their welcome at a sleepover: it’ll cut down your sleep time, lower its quality, and leave you wondering why you invited it in the first place.
- Want better sleep? There are ways, but mixing booze with certain sleep aids? That’s like adding Mentos to Coke — a risky explosion waiting to happen.
In this article we explore some scientifically backed methods to improve sleep when you’ve had a few drinks. Everyone needs to unwind on a Friday night, a drink or two (or three). Remember consuming an excessive amount of alcohol in a short period of time that results in a blood alcohol level of 0.08% or higher (>3-4 drinks) will effect sleep. So is there a way to make sure your Saturday is not affected while also enjoying Friday night?
Should You Avoid Drinking Alcohol?
We realize the simple answer is to not drink any alcohol at all. However, I/we do enjoy having a few drinks on the weekend with my wife and friends as I find it greatly enhances the social experience. I am beginning to train for a half marathon so obviously recovery will be very important.
That said, it’s strongly recommended that patients with sleep apnea abstain from all alcohol use. People often find quitting alcohol tough, especially occasional drinkers. Yet, avoiding it before bedtime is key. A sleep journal states that individuals who had their last drink FOUR hours before bedtime experience less distruptive sleep.

How does drinking alcohol mess with my sleep?
- Effects on Sleep: As alcohol levels drop later in the night, it leads to fragmented sleep and more vivid or stressful dreams.
- Diuretic Effect: Alcohol increases urine output, possibly leading to more awakenings.
- Effects on Breathing: Alcohol can increase snoring and is dangerous for those with obstructive sleep apnea.
- Interactions with Sleep Aids: Combining alcohol with sleep aids is cautioned against.
- Self-medication with Alcohol: Some use alcohol to combat insomnia, which can lead to problematic patterns.
- Recommendations: An “alcohol holiday” of at least two weeks is suggested, along with a buffer between drinking and bedtime.
- Effects on Morning Routine: Disrupted sleep due to alcohol may result in increased caffeine consumption the following day.
“REM sleep is the deepest state of sleep,” says Dr. Santos, “REM sleep is key to feeling fresh and healthy in the morning and is the most restorative part of sleep.” Alcohal reduces the amount of REM sleep you have at night.
After a drink, you may often find yourself snore more or louder. Alcohol is a muscle relaxant and disrupts your upper airway muscles, throwing off your breathing rhythm. For those with obstructive sleep apnea, it’s even riskier, causing frequent wake-ups as their airways play peek-a-boo.
Alcohol consumption leads to decreased sleep onset latency and changes in sleep architecture, especially early in the night when blood alcohol levels are elevated. Sleep characterized by slow delta activity (0.3 to 2 Hz) constitutes about 18% of the night. Alcohol consumption can lead to increased Slow Wave Sleep (SWS) in the first half of the night. This research was done by Melbourne School of Psychological science. After alcohol consumption, there’s decreased REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep in the first half of the night. (REM is the restorative part of sleep and is integral to rejuvenation.
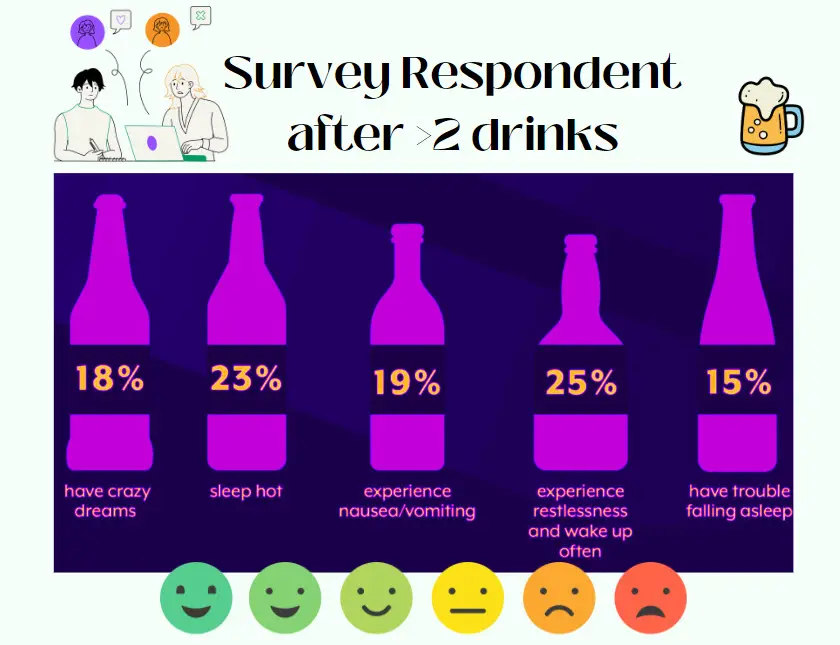
Young men, after consuming 0.8g/Kg dose of alcohol over nine nights (seven of them at home), showed specific changes in sleep patterns. With a BAC (Blood Alcohol Concentration) of 0.03 or 1.0%, SWS was significantly increased over the baseline on the first drinking night. Moderate alcohol consumption (0.55 g/kg) or around 2 drinks showed effects only in the first two hours of the sleep period. Alcohol inteferes several neurotransmitter systems important in the production of sleep. Even moderate drinking has an effect on sleep cycle. Below are results from a survey of 1000 respondents ( Men & Women over 18 years old).
Survey Results: Your Sleep Results after 2 drinks before bed time?
WAYS TO REDUCE NEGATIVE EFFECT ALCOHAL HAS ON SLEEP?
What are ways to (relatively) minimize the negative impact alcohol has on sleep? Water ? Electrolytes? Liquid between drinks? Should you have your last drink at a certain hour? There is no “cure-all” but there is definitely a recipe to make sure that sleep is disrupted to a minimum. We are talking about 2-3 drinks on a Friday or Saturday night.
The IMPROVE SLEEP FORMULA after DRINKS
- Drink earlier- Research says last drink 4 hours before sleep is ideal.
- drink a lot of water after and before sleep– Maybe some food as well to line your intenstine gut walls is not a bad practice
- Delay going to sleep until you’re not drunk
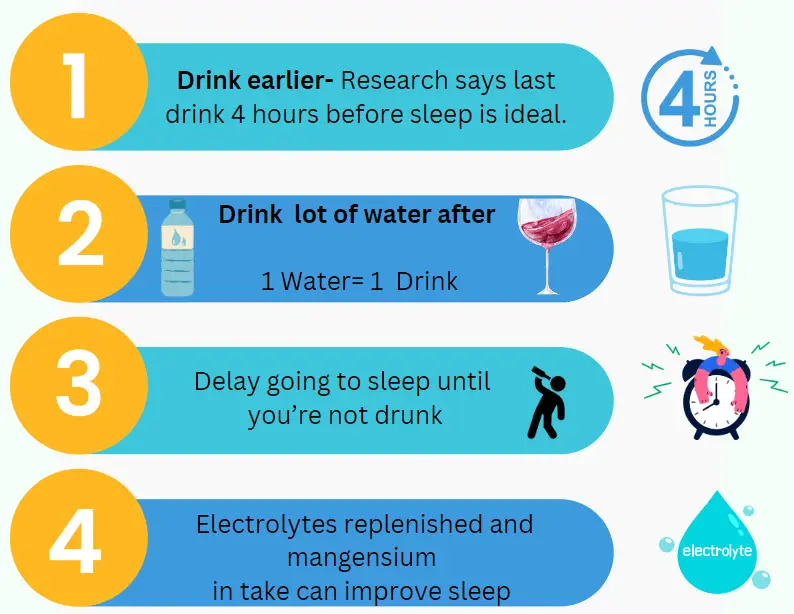
A simple rule of thumb when drinking is to drink an equal amount of water and booze, roughly at the same rate. If you have a bottle of electrolytes that you can carry and drink even better. Just keep the information on the “electrolyte bottle” under wraps while at the party, or you may come across as the “weird one”. Basically if you are having many drinks, we recomment to replenish electrolytes.
One of our Yoga Nidra students Andre, just went to a 3 days music festival, had 3-6 drinks each day, and zero hangover because he kept hishydration up. It was difficult to get alone or relaxation time, but everyday at some point I tried to put on my sound cancellation headphones and did some Yoga Nidra. “It just took 10 minutes a day and I felt more refreshed than the days I didnt do.” If you are time bound here is a quick 5 minute deep relaxation you can do.
TIPS ON How to improve sleep After a few drinks
- Limit Consumption: The most straightforward approach is to limit or avoid alcohol consumption, especially close to bedtime. If you do drink, try to do so in moderation. 4 HOURS before BEDTIME.
- Timing: If you choose to drink, do so earlier in the evening rather than right before bed. This gives your body time to metabolize the alcohol before you sleep.
- Stay Hydrated: Alcohol can dehydrate the body. Drink plenty of water alongside alcoholic beverages to stay hydrated and help flush the alcohol out of your system faster.
- Eat Before Drinking: Consuming food before or while drinking can slow the absorption of alcohol, which may reduce its impact on your sleep.
- Avoid Mixing: Mixing alcohol with caffeine or other stimulants can exacerbate sleep disturbances. For example, drinking wine with a caffeinated soda can make it harder to fall asleep.
- Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Use earplugs or a white noise machine if needed. This can help improve the quality of your sleep, even if it’s disrupted by alcohol.
- Limit Other Sleep Disruptors: Along with alcohol, avoid nicotine and heavy meals before bedtime. Both can disrupt sleep.
- Dont take Sleep Aids instead try a meditation or a Deep rest practice like NSDR or Yoga Nidra: Mixing alcohol with sleep medications can be dangerous. Try a deep rest sleep that will help you move faster in a state or relaxation,
- Monitor Your Sleep: If you’re concerned about how alcohol is affecting your sleep, consider using a sleep tracker. This can give you insights into your sleep patterns and how they might be influenced by alcohol consumption.

The Science behind non-conventional methods like Yoga Nidra on Alcohal?
Alcohal messes with your system. When we drink before bed our alcohal is in our system and as a result our liver enzymes metabolize alcohol causing us to not get deep sleep, get up more frequently and also inteferes with deep sleep which is eseential for restoration.
Practices like Yoga Nidra is backed by science can help bring in a state of deep rest, through body scans, breath control, and meditation, practitioners seek to cultivate harmony between the mind, body, and spirit. While the phsyical body or Biological body will definitely be under the duress of alcohal, the state of deep rest is associated with brain waves. If we are able to generate Theta Brain waves and move to this stage faster we can guarantee our body and mind a state of deep rest.
Unlike regular sleep, where one transitions from beta directly to delta, Yoga Nidra promotes an extended alpha state, which denotes relaxation. This form of relaxation ensures that you help your brain transition in to a state of relaxation faster somewhat negating the negative effect of alcohal.
Electrolytes is a Fast way to reduce alcohal effect
Water is great, coconut water even better. Basically Alcohal is tough on the liver and leaches out your electrolyte. Replenish electrolytes and the chances that your Morning will be fine is much higher.

FAQs: Sleep Vs Alcohal
Does Alcohol Help You Sleep?
While alcohol might induce sleepiness initially, it can disrupt deeper sleep stages later in the night. Especially disrupting REM Sleep. You can read more about this above.
Will a Small Amount of Alcohol Affect My Sleep?
First, what is small? Even 2 drinks effect sleep cycle. Moderate alcohol consumption (0.55 g/kg) or around 2 drinks showed effects only in the first two hours of the sleep period. Alcohol inteferes several neurotransmitter systems important in the production of sleep and puts your liver on overload. People with Sleep Apnea should try to stay away.
When should I should stop drinking before bed?
It’s best to wait at least 4 hours between your bedtime and your last drink to allow metabolism. While this maybe difficult, we recommend at least an hour. Flush yourself with lot of water to help you recover.
Why does alcohol make me sleepy?
Alcohol acts as a depressant, slowing brain activity, which can induce drowsiness. However, alcohal should not be confused as a replacement as a sleep inducer as it always will effect your sleep quality.
Why do I puff out air when I sleep?
This could be related to sleep patterns or conditions like sleep apnea. Consult your physician. With regards to drinking, alcohol is a muscle relaxant and disrupts your upper airway muscles, throwing off your breathing rhythm. For those with obstructive sleep apnea, it’s even riskier, causing frequent wake-ups due as it interrups breathing.
Alcohol and sleep?
Alcohol initially aids in falling asleep but disrupts the sleep cycle later on.
What is a drinker’s nose?
It’s a skin condition called rhinophyma, often wrongly attributed to heavy drinking.
Why does my period stop with alcohol?
Excessive alcohol can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting the menstrual cycle. Based on information from the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse a recent study found that greater than 35% of women with high alcohol consumption reported disruptions in their menstrual cycle. This happens as alcohol can briefly elevate testosterone and estrogen levels, disrupting the normal hormonal shifts that occur during ovulation
Have questions on deep rest or Yoga Nidra or want to book a session don’t hestitate from emailing us.