Symptoms and Solutions: Empowering Understanding and Healing for Somatic Symptoms
Somatic disorders encompass physical symptoms arising from psychological distress, often leading to confusion and frustration. Understanding these symptoms and their causes is vital in navigating Somatic Symptom Disorder (SSD).
In the realm of mental health, somatic symptoms present a unique challenge. Unlike physical ailments with clear medical explanations, somatic symptom disorder arises from psychological distress, blurring the lines between mind and body. This article aims to delve deeply into the landscape of somatic symptom disorder (SSD), exploring its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It is really important to first understand the source of this complex condition so that you can empower yourself with Somatic therapy to take the first step towards healing.
How to Identify Somatic Symptoms?
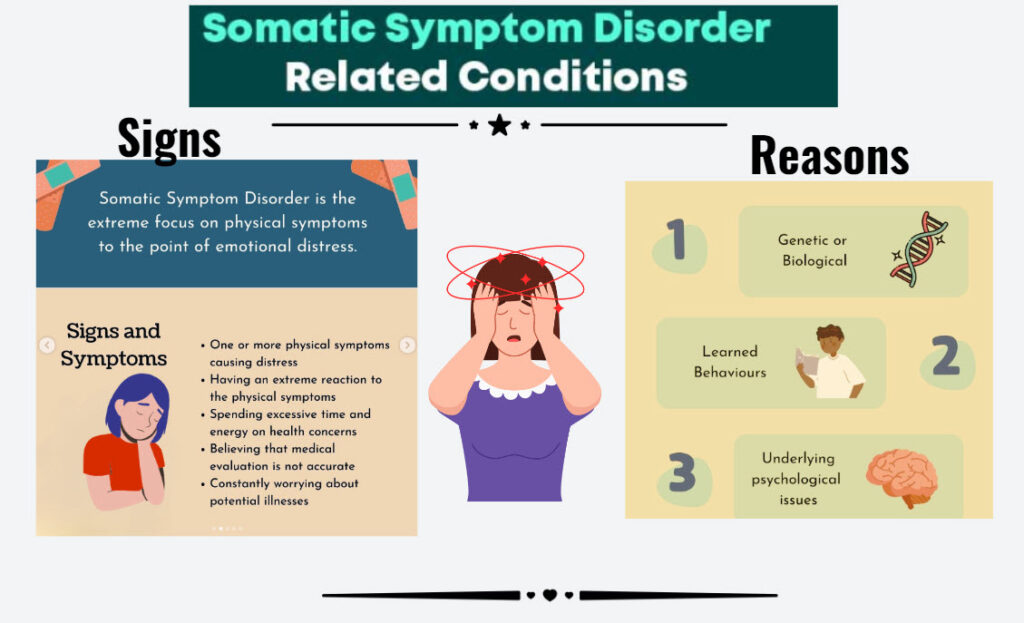
Somatic symptoms encompass a diverse range of physical manifestations, including pain, fatigue, gastrointestinal issues, and neurological symptoms. What distinguishes somatic symptoms from typical physical ailments is the absence of identifiable medical causes. These symptoms often perplex both patients and healthcare providers, leading to frustration and uncertainty. Whenever you see the first signs of these cropping up but know there is no medical ailment involved, examine what the symptoms are to take account.
Here are the list of manifestation and first Signs of the symptoms that may come up: (each case is different)
Somatic symptoms manifest in various ways, affecting different parts of the body and presenting as sensations or discomfort. This is the way the body talks to us. Headaches, muscle pain, dizziness, and shortness of breath are common complaints.
The onset of somatic symptoms typically coincides with periods of heightened stress, anxiety, or trauma. Individuals may notice a sudden increase in physical complaints without corresponding medical conditions, signaling the emergence of somatic symptom disorder. Don’t get worried if you see this happening. First check with your health care provider for medical symptoms. Once you’ve cleared it being a medical issue, then begin working on your mind.
What are the causes of Somatic Symptoms?
Somatic symptoms emerge in many different ways but once we have separated them from any medical challenges, we recognise their true nature- which involves complex interactions between psychological, biological, and social factors. Stress, trauma, and unresolved emotional conflicts often underlie the manifestation of somatic symptoms.
Additionally, personality traits, such as alexithymia, may influence the expression of somatic distress and their “triggers”. Sometimes a stressful or a humiliating situation can cause physical pain in the body. Now, one may think, how is this possible and what the connection between the two could likely be, but this is the first step to understanding the challenges that the ‘unseen threads of trauma and physical manifestation’ can hold. It is almost like preparing to undertake a journey into the unknown. Understanding the underlying “source causes” is crucial for effective treatment.
Certainly, somatic symptoms can manifest in various forms, and their root causes can be multifaceted. Here are more examples of somatic symptoms along with potential underlying causes:
1. Gastrointestinal Distress:
– Symptoms: Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation.
– Root Causes: Chronic stress, anxiety disorders (such as generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), food sensitivities or intolerances, past trauma affecting the gut-brain axis.
2. Cardiorespiratory Symptoms:
– Symptoms: Palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, or hyperventilation.
– Root Causes: Anxiety disorders (especially panic disorder), unresolved emotional trauma, history of cardiac events leading to health anxiety, or respiratory conditions like asthma exacerbated by stress.
3. Neurological Symptoms:
– Symptoms: Headaches, migraines, dizziness, tingling sensations, or numbness.
– Root Causes: Chronic stress, tension headaches due to muscle tension, migraines triggered by stress or hormonal fluctuations, somaticizing unresolved emotional conflicts into physical symptoms.
4. Musculoskeletal Pain:
– Symptoms: Back pain, joint pain, muscle stiffness, or tension.
– Root Causes: Prolonged stress leading to muscle tension and trigger points, unresolved emotional trauma manifesting as somatic pain, fibromyalgia characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain often associated with psychological distress.
5. Dermatological Symptoms:
– Symptoms: Rashes, hives, eczema flare-ups, or psoriasis plaques.
– Root Causes: Stress-induced exacerbation of skin conditions, psychosomatic skin disorders where emotional distress manifests as physical skin symptoms, autoimmune conditions aggravated by stress.
6. Genitourinary Symptoms:
– Symptoms: Pelvic pain, painful urination, or sexual dysfunction.
– Root Causes: Trauma history affecting pelvic floor muscles and nerves, stress-related exacerbation of interstitial cystitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, psychogenic erectile dysfunction or vaginismus.
These examples illustrate how somatic symptoms can affect various bodily systems and how their root causes may be influenced by psychological, emotional, and physiological factors. Addressing these root causes through holistic approaches such as somatic therapy, stress management, and trauma-informed care is essential for effective treatment and symptom management.
Treatment Options for Somatic symptom disorder
Addressing somatic symptom disorder requires a holistic approach that integrates both physical and psychological interventions.Different types of Somatic therapy, encompassing techniques like mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, aims to alleviate distress and improve coping mechanisms. Medication may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms or underlying mental health conditions. In addition, complementary therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, and massage therapy can supplement conventional treatment approaches. The intersection of Somatic work and yoga therapy is advancing exponentially to help healing in this space. Try a NSDR- Yoga Nidra practice for vitality here.
The 4 pillars of lifestyle must be looked at- diet, sleep, exercise and mindfulness practices can create a strong foundation for health and over and above this the treatment for somatic symptom disorder (SSD) will boost this change and wellbeing of the person concerned. Find approaches, considerations, effectiveness, and potential costs below:
1. Somatic Therapy:
– Approach: Somatic therapy focuses on the mind-body connection, aiming to address psychological distress through bodily experiences. Techniques may include body awareness exercises, sensorimotor psychotherapy, and somatic experiencing.
– Cost: Sessions with a licensed somatic therapist typically range from $100 to $250 per session, depending on location and therapist credentials. Some therapists offer sliding scale fees or accept insurance.
– Effectiveness: Somatic therapy can be highly effective in reducing somatic symptoms and improving overall well-being. Research suggests that it may lead to significant improvements in symptoms and functioning over time.
– Duration: Treatment duration varies depending on individual needs and goals. Some individuals may experience relief after a few sessions, while others may benefit from longer-term therapy.
2. Mindfulness and Relaxation Exercises:
– Approach: Mindfulness-based techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, neuro linguistic programming and progressive muscle relaxation, promote relaxation and stress reduction. These practices encourage present-moment awareness and acceptance of bodily sensations.
– Cost: Mindfulness and relaxation exercises can be learned through books, online resources, or attending classes. Costs may include purchasing books, online course fees, or attending workshops.
– Effectiveness: Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing somatic symptoms, anxiety, and depression. Regular practice can lead to improved stress management and enhanced well-being.
– Duration: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation exercises regularly, ideally daily, can yield long-term benefits. Initially, individuals may notice improvements in symptoms within a few weeks to months of consistent practice.
3. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
– Approach: CBT focuses on identifying and challenging maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors contributing to somatic symptoms. It helps individuals develop coping strategies, problem-solving skills, and more adaptive ways of thinking.
– Cost: Sessions with a licensed CBT therapist range from $100 to $250 per session. Many therapists accept insurance, and some offer sliding scale fees.
– Effectiveness: CBT is considered one of the most effective treatments for somatic symptom disorder. Research indicates that it can lead to significant reductions in symptom severity and improvements in functioning.
– Duration: CBT typically consists of 12 to 20 sessions, although the duration may vary depending on individual needs and treatment progress. Check with your healthcare provider before signing up for any sessions.
4. Medication:
– Approach: Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with somatic symptom disorder, such as antidepressants for depression or anxiety, pain relievers for chronic pain, or medications targeting specific symptoms like insomnia or gastrointestinal distress.
– Cost: The cost of medication varies depending on the type, dosage, and whether generic or brand-name drugs are prescribed. Many insurance plans cover prescription medications, reducing out-of-pocket costs for patients.
– Effectiveness: Medication can be effective in managing symptoms, particularly when used in conjunction with psychotherapy. It may help alleviate distressing symptoms and improve overall functioning.
– Duration: Treatment duration with medication varies depending on the individual’s response, symptom severity, and ongoing treatment plan. Some individuals may require long-term medication management, while others may use medication for shorter periods.
5. Complementary Therapies:
– Approach: Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, yoga nidra– nervous system reset, massage therapy, and chiropractic care can complement conventional treatment approaches for somatic symptom disorder. These therapies focus on promoting relaxation, reducing stress, and restoring balance to the body. Find a short practice session to relax you here.
– Cost: Costs vary depending on the type and frequency of therapy. Acupuncture sessions typically range from $50 to $150 per session approx, yoga classes may cost $10 to $20 per class minimum, and massage therapy sessions range from $50 to $150 per hour.
– Effectiveness: Complementary therapies can be beneficial in reducing stress, improving relaxation, and relieving physical tension associated with somatic symptoms. They may enhance overall well-being and quality of life.
– Duration: The duration and frequency of complementary therapies depend on individual preferences and treatment goals. Some individuals may benefit from regular sessions, while others may use these therapies as needed for symptom management.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness and duration of treatment can vary significantly depending on individual factors such as symptom severity, co-occurring mental health conditions, treatment adherence, and the quality of the therapeutic relationship. Additionally, accessing affordable treatment options may be a barrier for some individuals, so it’s essential to explore available resources such as community mental health centers, sliding scale therapy options, and online therapy platforms. A comprehensive and individualized treatment plan that addresses both physical and psychological aspects of somatic symptom disorder is key to achieving long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Empowering Through Knowledge:
Empowerment lies at the heart of navigating somatic symptom disorder. Educating oneself about the condition, its symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for informed decision-making. Seeking support from healthcare professionals who specialize in somatic disorders can provide guidance and validation. Engaging in self-care practices, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques, empowers individuals to take an active role in their healing journey.
Challenges and Coping Strategies for Somatic Disorders
Living with somatic symptom disorder poses significant challenges, including stigma, invalidation, and difficulty accessing appropriate care. Coping strategies, such as building a support network, practicing self-compassion, and setting realistic goals, can help navigate these obstacles. Developing resilience and cultivating a positive mindset are essential for coping with the ups and downs of managing somatic symptoms. Trusting the process and allowing the health care providers to guide you through these methods- especially the healing through activation of subconscious mind, can hasten the recovery process, but one’s mindset has to be open to it.
Navigating somatic symptom disorder requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the complex interplay between mind and body. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options associated with SSD, individuals can empower themselves to embark on a path towards healing and recovery. Through education, support, and self-care, individuals can reclaim agency over their health and well-being, transforming the journey from one of uncertainty to one of empowerment and resilience.